Shoulder Injury and Rehabilitation: A Guide to Recovery and Resilience
The shoulder, one of the most mobile joints in the body, is essential for countless daily activities and athletic movements. Its unique range of motion, however, also makes it prone to injuries. Whether caused by overuse, poor posture, or trauma, shoulder injuries can significantly impact quality of life. Understanding these injuries and their rehabilitation process is key to regaining function and preventing future issues.
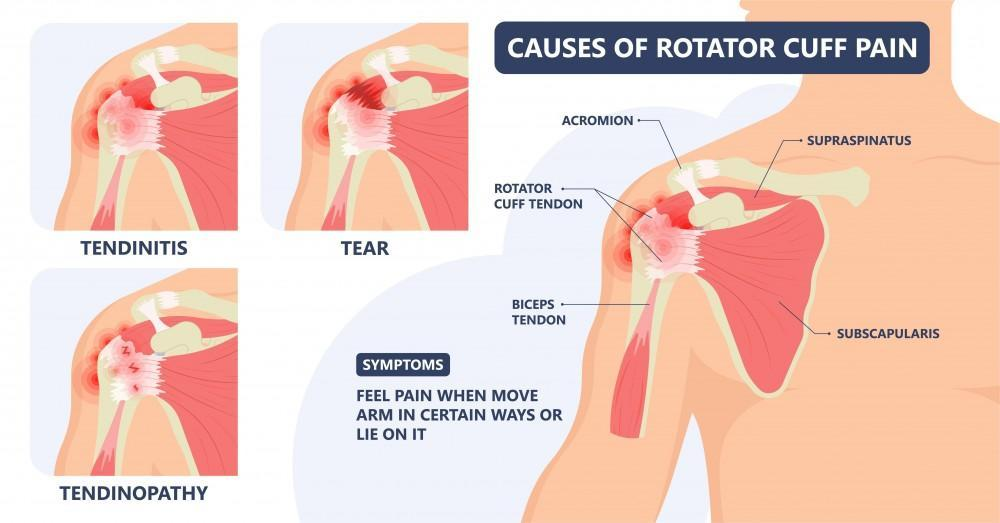
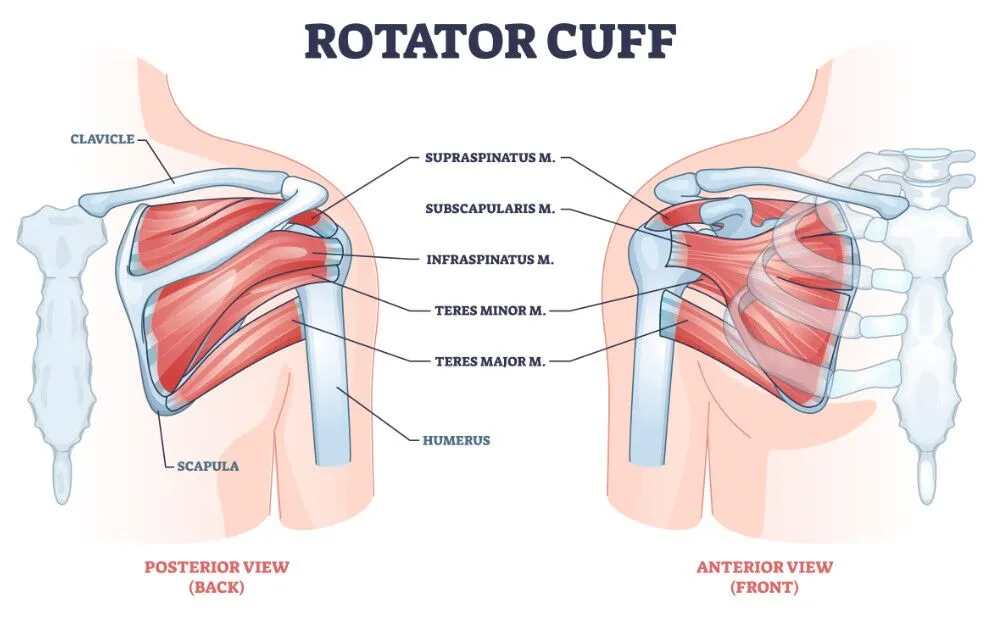
Common Shoulder Injuries
- Rotator Cuff Injuries
- Cause: Repetitive overhead motions or acute trauma.
- Symptoms: Pain, weakness, and difficulty lifting the arm.
- Shoulder Impingement
- Cause: Compression of tendons or bursa during overhead activities.
- Symptoms: Pain when lifting the arm or reaching above shoulder height.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
- Cause: Inflammation of the shoulder joint capsule, often after immobility.
- Symptoms: Gradual stiffness and reduced range of motion.
- Dislocations and Instability
- Cause: The shoulder joint slipping out of its socket due to trauma or weak structures.
- Symptoms: Severe pain, swelling, and visible deformity.
- Labral Tears
- Cause: Damage to the cartilage surrounding the shoulder socket from overuse or sudden impact.
- Symptoms: Clicking sounds, pain, and decreased strength.
Rehabilitation for Shoulder Injuries
Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in restoring shoulder function and preventing further damage. A comprehensive rehab program includes:
- Pain Management
- Use of ice, heat, and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Techniques like massage therapy or dry needling to relieve muscle tension.
- Range of Motion Exercises
- Gentle movements like pendulum swings and arm stretches to restore mobility.
- Strengthening Exercises
- Targeted exercises for the rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers, such as resistance band workouts.
- Postural Correction
- Education on maintaining proper posture to reduce stress on the shoulder joint.
- Physiotherapy
- Hands-on techniques from a physiotherapist to improve joint mobility and alleviate stiffness.
- Sports-Specific Training
- For athletes, rehabilitation includes drills to rebuild strength and coordination for their sport.
Preventing Shoulder Injuries
- Warm-Up Properly: Always include dynamic stretches and mobility exercises before physical activity.
- Strengthen Supporting Muscles: Regularly train the rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers.
- Use Proper Technique: Ensure correct form during exercises and sports activities.
- Avoid Overuse: Take rest days and cross-train to prevent repetitive stress on the joint.
- Maintain Good Posture: Avoid slouching to minimize strain on the shoulders.
When to Seek Help
If shoulder pain persists, worsens, or is accompanied by swelling, numbness, or limited motion, consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention with physiotherapy or medical treatment can prevent further complications and speed up recovery.
Conclusion
Shoulder injuries can be debilitating, but with the right approach to rehabilitation, recovery is achievable. Combining pain management, tailored exercises, and preventive strategies ensures not only healing but also long-term resilience. Whether you’re an athlete or someone recovering from a strain, taking proactive steps toward shoulder health can lead to a stronger, pain-free future.
