Core Series 2 of 3: Neck Core
As we continue the Core Series, part 2 of the Core series discusses the core muscles of the neck.


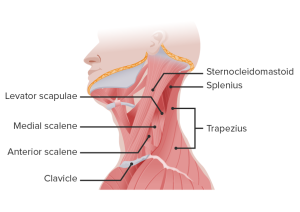
The neck’s core muscles are essential for head support, neck stability, and posture. These muscles work together to stabilize the cervical spine and support upper body alignment. Here’s a summary of the primary neck muscles and their functions:
1. Deep Cervical Flexors
- Key Muscles: Longus Colli and Longus Capitis
- Function: Stabilize and flex the neck, aiding in proper head posture and cervical alignment.
- Importance: Weakness can lead to forward head posture and related neck pain.
2. Suboccipital Muscles
- Key Muscles: Rectus Capitis Posterior Major/Minor, Obliquus Capitis Superior/Inferior
- Function: Control fine head movements, extend and rotate the head.
- Importance: Rich in proprioceptors, vital for head balance and spatial awareness.
3. Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)
- Function: Flexes, rotates, and tilts the head.
- Importance: Often tense due to poor posture; tightness can cause headaches and neck discomfort.
4. Scalene Muscles
- Key Muscles: Anterior, Middle, and Posterior Scalene
- Function: Assist with side-bending, rotation, and breathing.
- Importance: Tightness may cause nerve impingement, contributing to thoracic outlet syndrome.
5. Levator Scapulae
- Function: Elevates scapula, stabilizes neck and shoulder.
- Importance: Prone to tightness, which can lead to neck stiffness and upper back pain.
6. Upper Trapezius
- Function: Extends and laterally flexes the neck, stabilizes head and shoulders.
- Importance: Tension here can cause neck and shoulder pain, as well as headaches.
7. Splenius Capitis and Cervicis
- Function: Extend, rotate, and laterally bend the neck.
- Importance: Help maintain posture and stability, especially for looking up or rotating the head.
8. Semispinalis Capitis and Cervicis
- Function: Aid in neck extension and stabilize the cervical spine.
- Importance: Support head posture and reduce neck strain.
9. Rotatores and Multifidus (Deep Spinal Muscles)
- Function: Stabilize each cervical vertebra and aid in small, controlled movements.
- Importance: Crucial for cervical stability and alignment.
Core Neck Muscle Functions:
- Stabilization: Key deep muscles like the longus colli and multifidus maintain cervical spine alignment.
- Flexion & Extension: Muscles such as the SCM and trapezius contribute to neck bending.
- Rotation & Lateral Flexion: Muscles like the SCM, scalenes, and splenius allow side-to-side movement.
- Proprioception: The suboccipitals provide feedback for head positioning and balance.
These muscles enable neck mobility, support posture, and help prevent neck strain. Proper strength and flexibility in the neck’s core muscles are essential for head and spine alignment and reducing neck pain.

