Easy Guide To Common Causes of Back Pain

Back pain is a prevalent issue caused by a variety of lifestyle habits, medical conditions, and environmental factors. Prolonged poor posture, lack of activity, and repetitive movements are often key contributors. Here’s a simplified look at common causes of back pain, their implications, and preventive strategies.
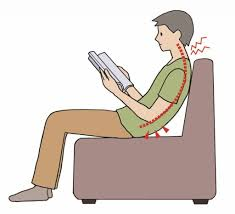
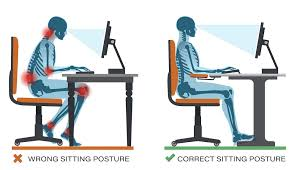
1. Poor Posture
-
- Description: Slouching while sitting or standing can misalign the spine, placing undue stress on muscles and ligaments.
- Prolonged desk work or phone use leads to (among other issues)
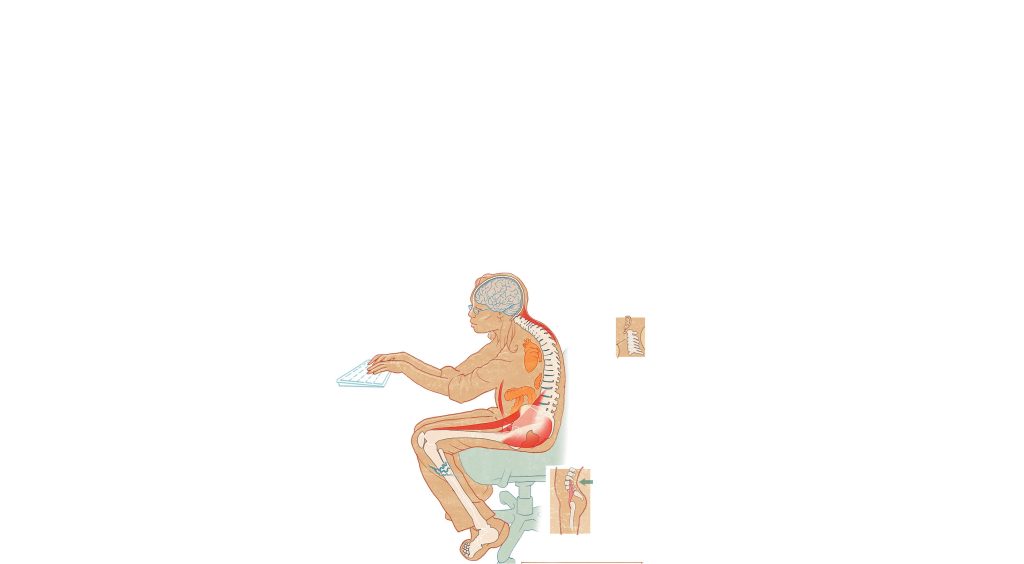
When we move around, soft discs between vertebrae expand and contract like sponges, soaking up fresh blood and nutrients. But when we sit for a long time, discs are squashed unevenly. Collagens harden around supporting tendons and ligaments.
People who sit more are at greater risk for herniated lumbar discs. A muscle called the psoas travels through the abdominal cavity and, when it tightens, pulls the upper lumbar spine forward. Upper-body weight rests entirely on the ischial tuberosity (sitting bones) instead of being distributed along the arch of the spine.
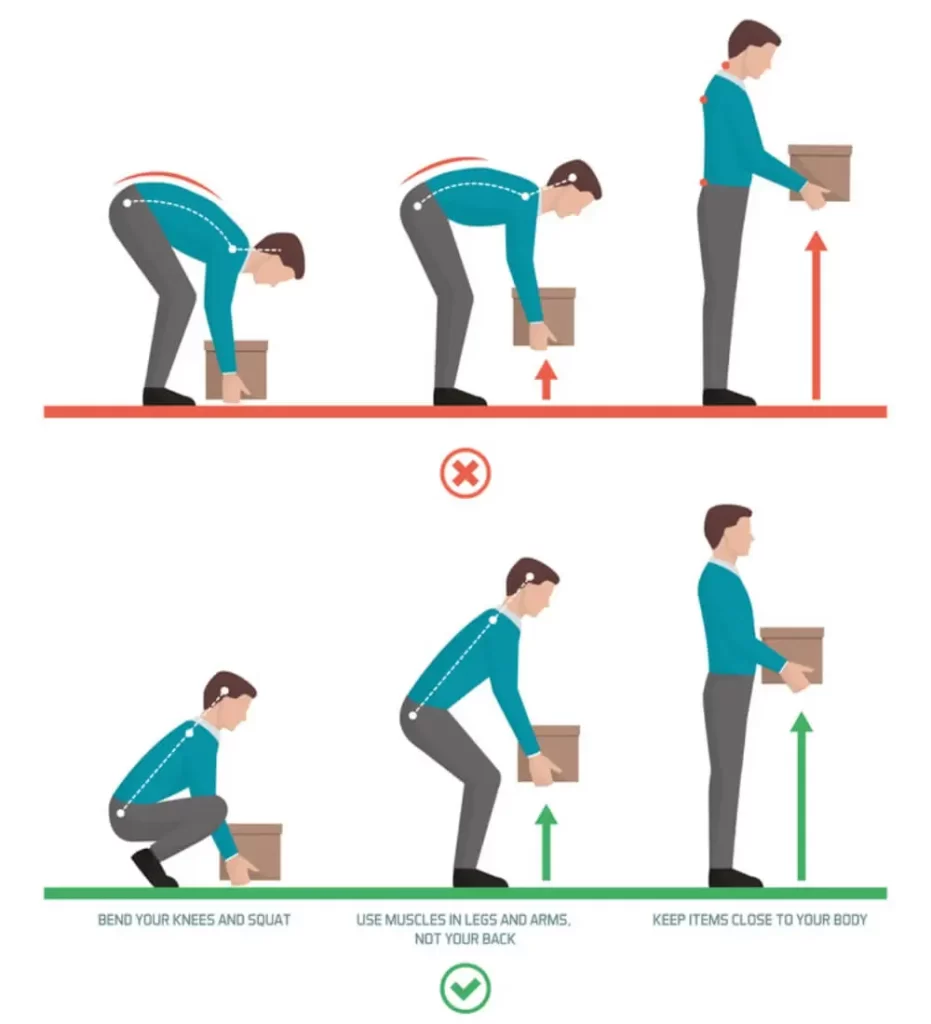
2. Muscle Strain or Ligament Sprain- Description: Sudden movements, improper lifting techniques, or overuse can strain muscles and ligaments.
Example
-
- : Experiencing sharp lower back pain after lifting heavy luggage.
3. Prolonged Sitting and Sedentary Lifestyle
- Description: Sitting for extended periods weakens core and back muscles, leading to poor spinal support.
- Example: Lower back stiffness after working long hours without breaks.
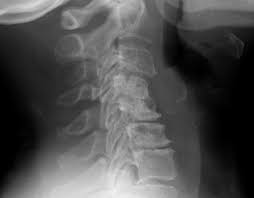
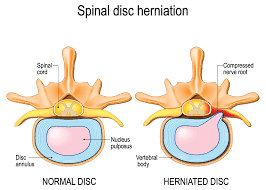
4. Herniated Discs
- Description: The soft center of a spinal disc protrudes, pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain and long term damage if not resolved.
- Example: Sciatica or shooting leg pain due to nerve compression from a herniated disc.
5. Stress and Muscle Tension
- Description: Emotional stress can cause muscle tightness, particularly in the neck and upper back.
- Example: Experiencing back pain during a high-pressure workweek.
6. Lack of Physical Activity
- Description: Inactivity reduces muscle strength and flexibility, increasing the likelihood of back injuries.
- Example: Increased back discomfort after months of avoiding exercise.
7. Medical Conditions
- Common Conditions:
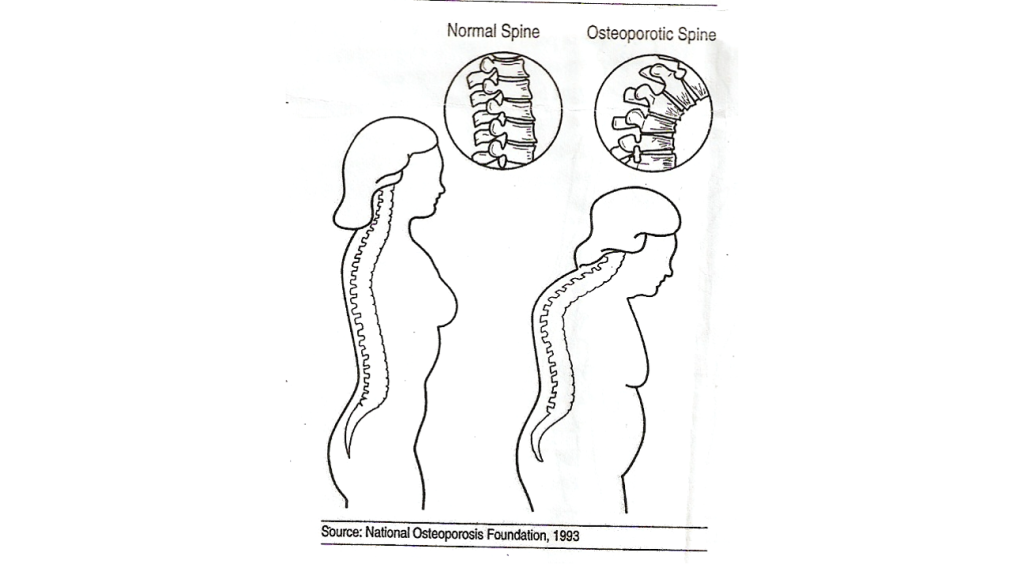
- Osteoporosis: Fragile bones leading to spinal compression fractures.
Wedge Fractures
-
- Arthritis: Joint inflammation causing stiffness and back pain.
-
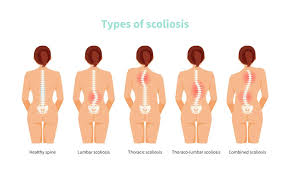
- Scoliosis: Abnormal spinal curvature resulting in uneven weight distribution.
- Example: Chronic back pain worsened by osteoporosis in older adults.
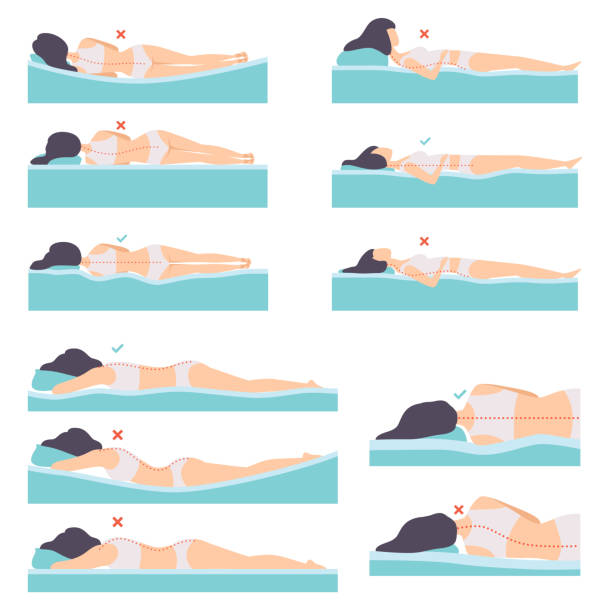
8. Sleeping Positions and Poor Support
- Description: Unsupportive mattresses or improper sleeping positions can strain the back.
- Example: Waking up with back pain after sleeping on a soft, sagging mattress.
Preventive Measures
- Maintain Good Posture: Use ergonomic chairs and adjust screens to eye level to avoid slouching.
- Strengthen Core Muscles: Engage in exercises like Pilates or yoga to improve spinal support.
- Lift Properly: Bend at the knees and keep heavy objects close to the body when lifting.
- Take Breaks: Avoid prolonged sitting by standing and stretching every 30 minutes.
- Sleep Smart: Use a firm mattress and maintain a neutral spine while sleeping.
By identifying and addressing these common causes of back pain, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce discomfort, enhance mobility, and support long-term spinal health.

